What is ultrasound?
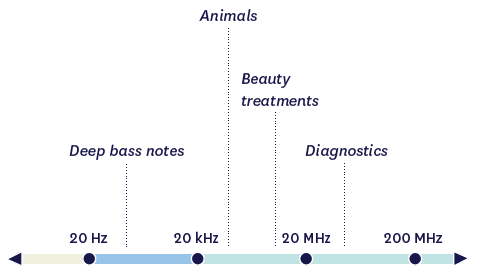
Ultrasound is a sound wave outside of the human audible range
The lower and upper limits of frequencies audible to the human ear are 20 Hz to 0,000 Hz.
Ultrasound exceeds the limit of 20 kHz. High-frequency ultrasound cosmetic treatments are, as a rule, in the 1 MHz to 10 MHz range, allowing them to reach different skin layers.
How is ultrasound generated?
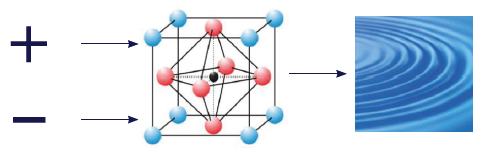
Ultrasonic waves are generated by means of piezo-ceramic transducer systems.
The piezo-ceramic element, which is typically a quartz crystal, has the ability to move its atoms as soon as AC voltage is applied. This is called a reverse piezoelectric effect. The movement of the atoms generates the ultrasound wave.
How does ultrasound penetrate the skin?
Air is an excellent ultrasound wave dampener. However, liquids minimally block ultrasound and the waves can spread rapidly.
This is why a coupling medium is always required for transmitting ultrasound waves into the skin.
The most suitable coupling medium is a gel that will remain on the skin longer. Using one enables the ultrasonic waves to penetrate the skin during a treatment optimally. To ensure airtight and excellent transmission, the ultrasound gel should be applied as generously as possible. For this reason, a skin contact detection sensor is integrated into the IONTO-SONO Intense handpieces: they only emit ultrasonic waves after skin contact has been 100% established. If the skin contact detection sensor is switched on, you will see by the continuously lit LED strip that you have made contact with the skin. Please note: The higher the frequency of the programme you are using, the more sensitive the skin contact detection sensor.
Ultrasound parameters
The parameters that influence the treatment’s efficacy and penetration depth are frequency, mode, intensity and duration.
1. Ultrasound frequency
2. Mode
3. Intensity
4. Time
Frequency
is indicated in Hz = hertz, MHz = Mega Hertz or GHz = Giga Hertz. It describes how many ultrasound oscillations are emitted per second:
→ 1 MHz = 1 million oscillations per second
→ 3 MHz = 3 million oscillations per second
→ 10 MHz = 10 million oscillations per second
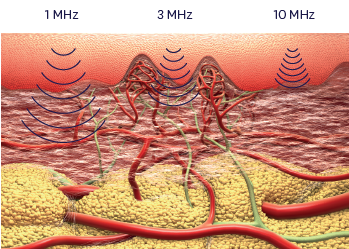
Each frequency has a wavelength. The wavelength is the distance between the two amplitudes. The frequency of the ultrasonic waves determines the wavelength and depth of penetration as half-value penetration depth. Half-value penetration depth indicates the depth at which 50% of the emitted power is received.
The higher the frequency – the smaller the wavelength. The smaller the wavelength – the lower the penetration depth:
→ 1 MHz = Wavelength 1.5 mm (λ1) → approx. 3.0 cm half-value penetration depth
→ 3 MHz = Wavelength 0.5 mm (λ3) → approx. 1.0 cm half-value penetration depth
→ 10 MHz = Wavelength 0.15 mm (λ10) → approx. 0,3 cm half-value penetration depth
Intensity
Intensity is the acoustic power per surface unit that penetrates an area.
The unit of intensity is described as power per area: [W/ cm2]
Intensity also has an influence on the wavelength. Important: The higher the intensity, the lower the wavelength. The higher the intensity, the higher the amount of heat generated:
→ Low = 0.1 – 0.3 [W/cm2]
→ Medium = 0.4 – 0.8 [W/cm2]
→ High = 0.8 – 2.0 [W/cm2]
Mode
The mode indicates whether a continuous sound or a pulse sound is being emitted.
– Continuous sound: Permanent emission (Cont. mode) → Intense thermal action
– Pulse sound: Sound with controlled pauses → reduced thermal action
Mode (Cont.) Permanent emission 100% sound
Mode 1:3 oooo → 1 ms sound, 3 ms pause (25% sound)
Mode 1:5 oooooo → 1 ms sound, 5 ms pause (16% sound)
Mode 1:10 oooooooooo → 1 ms sound, 10 ms pause (9% sound)
Depending on the treatment program, skin type and skin condition, various default modes are programmed.
– Continuous sound is suitable for atrophic, normal or robust skin.
– Pulse sound is suitable for sensitive skin types and skin with blemishes or couperose since the pauses at intervals mean less heat is generated in the tissue.
How does ultrasound work?
The ultrasound used in cosmetics applications has Thermal, Mechanical and Biochemical effects.
Its Thermal action has a stimulating effect on blood flow and activates cell metabolism.
Alternating pressure and vacuum phases generate the Mechanical action.
The Biochemical effects trigger a micro-massage in the tissue, which influences the fibroblasts and stimulates the formation of new collagen. Due to the oscillation amplitude, more active substances can penetrate the skin’s barrier and its cellular absorption capacity increases.
Three frequencies: 1 MHz / 3 MHz / 10 MHz
with a triple effect
